Seit nun fast 4 Monaten betreiben wir unseren Online-Shop nicht mehr mit Magento, sondern mit PrestaShop. Dies bringt bereits ein Google-Analytics Plugin mit. Man gibt nur die Web-Property-ID ein und los geht’s.
Nachdem wir die Daten nun auswerten wollten, sind uns zwar die Nutzerzahlen zu den Vormonaten plausibel erschienen, jedoch waren alle Aufrufe in die Systemeigenen URLs gepackt.
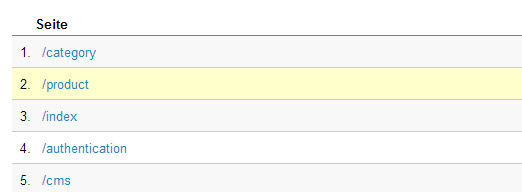
So waren alle Produktaufrufe in /product und alle Kategorieklicks in /category gebündelt eingeordnet. Dies nützt ein natürlich wenig, wenn man genau sehen will, welches Produkt sich gut verkauft und welches nicht.
Mit wenigen Änderungen am Sourcecode des Google-Analytics Moduls behebt man jedoch diesen „Fehler“:
- auf den Shopserver verbinden
- in das Verzeichnis von PrestaShop wechseln
- in das Verzeichnis modules/ganalytics/ wechseln
- die Datei ganalytics.php vorher sichern
- ganalytics.php mit einem Editor der Wahl öffnen
- folgenden Abschnitt suchen
$file = str_replace(array('.php', '-'), '', basename($_SERVER['SCRIPT_NAME']));
- um folgenden Code ergänzen
if($file == "category" ||
$file == "product" ||
$file == "search" ||
$file == "cms" ||
$file == "index") {
$file = $_SERVER["REQUEST_URI"];
}
- noch einmal kontrollieren
$file = str_replace(array('.php', '-'), '', basename($_SERVER['SCRIPT_NAME']));
if($file == "category" ||
$file == "product" ||
$file == "search" ||
$file == "cms" ||
$file == "index") {
$file = $_SERVER["REQUEST_URI"];
}
- speichern
- fertig
Schon am nächsten Tag sammelt Google-Analytics die richtigen URLs ein.


 Last week, the creators of NConf, a new Nagios configuration tool, released a new version.
Last week, the creators of NConf, a new Nagios configuration tool, released a new version.