What is NagiosGrapher?
NagiosGrapher is a Nagios add on which automatically generates performance charts and graphs from returned Nagios values. It takes the raw Nagios data and turns it into normalised values administrators can analyse, either on its own or Nagios’ web interface.
NagiosGrapher and NETWAYSGrapherV2 – what’s the difference?
They use a completely different architecture. NagiosGrapher is the predecessor to NETWAYSGrapherV2, but as it is so popular in the community, we decided to keep the project running. We’ve invested the latest technologies in the NETWAYSGrapherV2 however, and that is our main ‘grapher’ project.
How does it work?
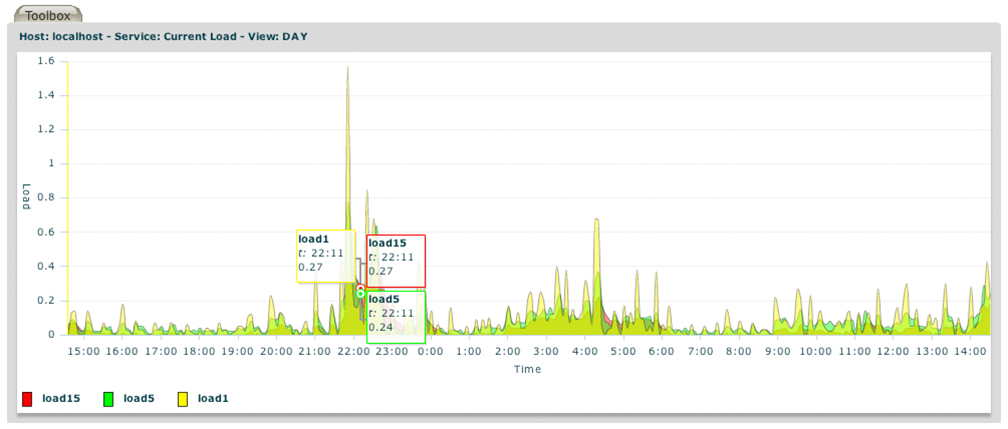
Nagios plugins run checks on hosts and services, returning results in strings of extended information. The NagiosGrapher daemon receives these via perf-files or a pipe, filters them of numeric data by using regular expressions and stores the data in a RRD (Round Robin Database). The functions we built use the RRD to create graphs from the data values and are generated on request – in real-time (or within 5 min). All interaction can be made on a Perl CGI based front end, or through the Nagios system itself.
Any interesting features?
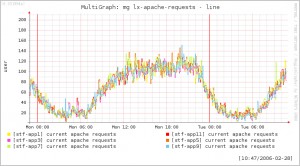
Aside from the real-time graphing as mentioned above, NagiosGrapher also does ‘Mulit-graphs’. Several different graphs can be brought together and displayed in one view, which is quite handy when analysing multiple switch ports for example.
NagiosGrapher also features a ‘process-service-perfdata’ interface, so no patches or changes to the Nagios system needs to be made. This ensures that it is easy to install and maintain. Unlike some other programs, you don’t need to repeat installations because it automatically recognises new devices and services, incorporating their monitoring values for graphing. And because it runs on RRD with automated data cleanup, the database stays at a fixed size, keeping the backend slim.
What is the ‘process-service-perfdata’ interface exactly?
This is an extra specialised interface between Nagios and the RRD where the returned Nagios performance values are normalised. Because it acts as a kind of translation device, no patches or alterations need to be made to Nagios itself, making installation and operation much smoother.
NagiosGrapher is one of the most popular, longstanding graphing tools for Nagios, alongside nagiosgraph and PnP. Where PnP is easier and faster to configure, it only reads perfdata. NagiosGrapher is more complex but can check older plugin output, and breaks into components easily, thus being also more flexible. This makes it fantastic to scale and implement in large environments.
Any plans for further developments?
NagiosGrapher has been around for quite a while now, but at least it’s reliably stable and very robust. Basically, we’ll keep with maintenance and patches but really our main development work is on the NETWAYSGrapherV2 – speaking of which, we have just released the RC1.
NagiosGrapher in a nutshell?
The old-timer basic Grapher for reliable performance charts, easy to install, easy to maintain and good for large environments – but not as dynamic as the new NETWAYSGrapherV2!
More information:
Join the project or download
NETWAYS Blog
Ask the developer: NETWAYSGrapherV2
What is NETWAYSGrapherV2?
NETWAYSGrapherV2 is the newest graphing addon for Nagios and any other software. It plots charts and graphs automatically from returned Nagios plugin output, so administrators can make performance analyses of their network and applications easier.
How does it work?
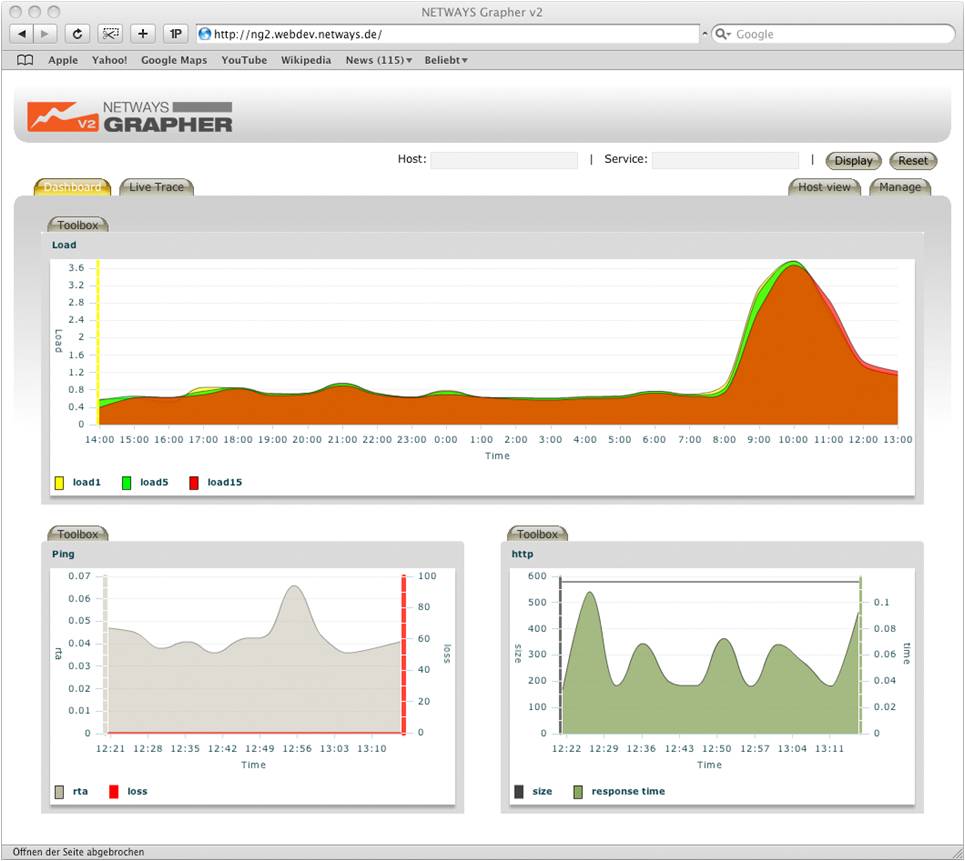
Plugin output, perf data, PIPE interface and TCP protocol from any software such as Nagios are received by a collector daemon. Here the data is parsed to filter out numeric values automatically, which are then sent to the MySQL database. When a user requests a graph on the web interface front end, the Grapher API retrieves data from the database and creates graphs though the charting engine developed on Adobe Flex.
Why Adobe Flex?
Adobe Flex is very powerful tool for graphing – it allows us to create “real” real time graphs, where the user can watch the chart change with the flow of data. It allows the user to mouse over individual time points to get specifics.
What’s different about this grapher?
Aside from the “real” real time charts, the dashboards and automated housekeeping are pretty exclusive.
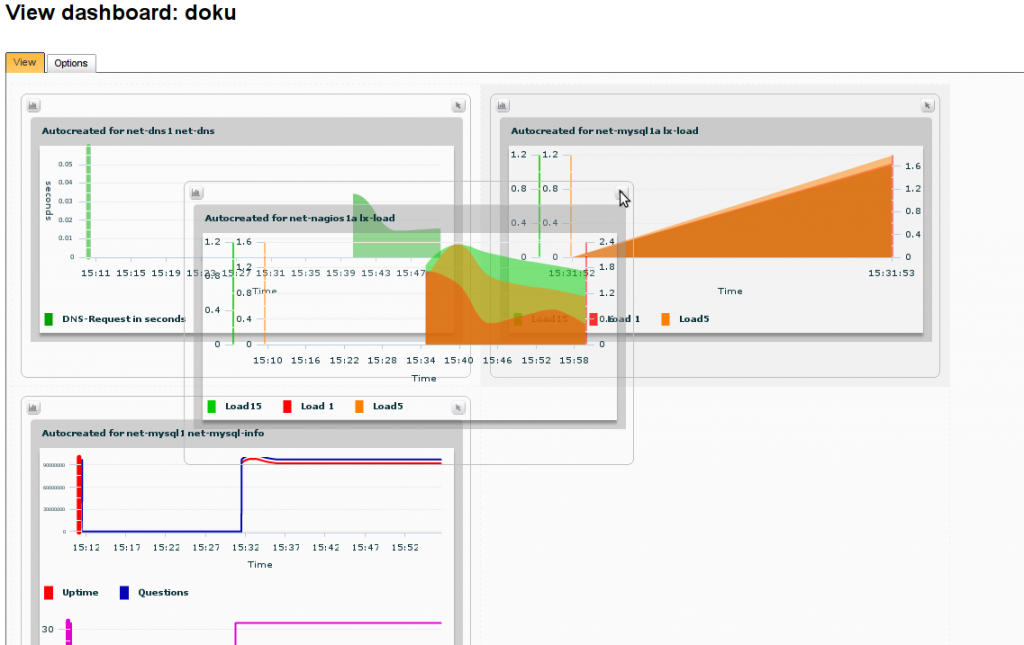
Dashboards allow the user to set multiple graphs they need for their daily tasks onto one ‘screen set’ for easy viewing – which can be shared with other users too.
The collected data is automatically aggregated in to hourly, weekly, monthly or yearly sets in an ongoing housekeeping in the background so they can be easily called up later for graphing.
How does it compare to other graphing tools?
Nothing compares to it when it comes to handling, display and useability – nothing that we have seen out there so far.
What about useability?
Well, there are a few user friendly features such as the ‘drag & drop’ multi-graphs, Ajax search, and different display methods with navigation toggle and full view functions.
With the ‘drag & drop’ multi-graphs, the user can compare for example the bandwidths of two machines by simply clicking on one chart and dropping it on the other.
Also, users can essentially manage themselves because all user and user group management is done through the web interface. That’s really handy for larger companies with many administrators or for managed services companies to offer customers views of their Nagios systems.
Do you have a favourite feature or tool?
The new collector daemon is cool and took a lot of work – it automatically filters values out of the plugin or perfdata without the user needing to code a thing.
And then of course the Adobe Flex charts – it’s simply the new way to display graphs.
What’s the outlook?
We believe management should be kept simple – so we want to reduce the amount of manual back end work the user has to do, by making everything accessible through simply clicking on the web interface. That, and speed up the performance of the collector – there’s always room to improve!
NETWAYSGrapherV2 in a nutshell?
It’s really the next generation grapher – genuinely real time, flexible and user friendly to a click.
More information:
Join the project or download
Ask the developer: NoMa for Nagios
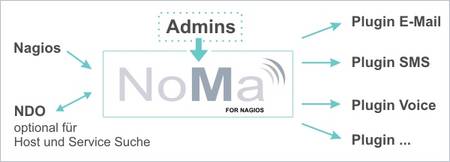
What is NoMa?
Short for Notification Manager, it is an online tool for managing contacts and the Nagios notifications they receive. It offers easy administration of contacts, groups and escalations, taking into account working hours, time zones and even holidays.
Who is NoMa useful for?
NoMa is great for environments which have many contacts, hosts, services etc., and whose contacts should receive different notifications. If I could create a ‘Nagios Enterprise Suite’ for data centers, large and international corporations- then NoMa would definitely be in there.
How does it work?
NoMa on its own is simply consists of a MySQL database, lookup scripts and notification scripts, and the whole thing is connected to Nagios as a normal plugin.
The user enters contacts, groups and their respective notification requirements via the online interface to be stored in the database. In entering notification requirements, NoMa queries the NDO and gives an Ajax search preview.
When Nagios registers an error, it notifies NoMa. Then NoMa looks up the notification, contact, escalation level, dates or times and alert methods that match, and forwards the Nagios alert to the right person or people. All sent notifications then are available on a log viewer.
In essence we have outsourced the notifications component of Nagios to NoMa.
What communication channels can be used?
Any! The NoMa download comes with notification scripts for email, voicemail and SMS. The great thing about NoMa is that it is easily extendable – I imagine that an IM script exists somewhere already.
How is NoMa’s user administration?
NoMa has really flexible access management system, avoiding the glitch so many softwares have, that only one single administrator has access rights. Multiple users can edit notifications, but it is also easily customised to enable for example, low level administrators the chance to edit their own or group’s notification details, but nothing else.
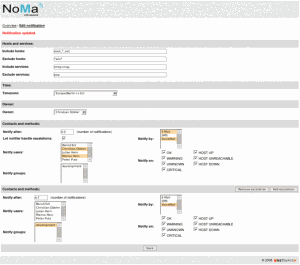
The use of wildcard characters to define hosts and services for notification recipients – not only can the user search hosts and services by typing the first few letters to call up a list of matches, but they can also define them with wildcards for configuration. NoMa can essentially find and configure notifications from an unlimited number of hosts and services, without the administrator needing to know their names. Even better, you can search and define on multiple terms and make exclusions all in one hit. Just wildcard definitions alone make NoMa incredibly useful for large environments.
NoMa in a nutshell?
Basically NoMa makes sure that the right notifications go to the right people at the right times – but instead of typing in config files, you can do it all through a few clicks on NoMa. It makes life easier, taking the ‘manual work’ out of configuring notifications in Nagios. Easy admin for the admins!
More information:
Features & demo system
Join the project or download
Ask the developer: EventDB for Nagios
What is EventDB?
EventDB is an event handler for Nagios which filters traps and logs. It extends on standard Nagios monitoring to check traps and logs for errors from software components and network devices.
How does it work?
Software such as Linux or Windows generate log files and other events that are not machine parsable. EventDB consists of a web interface, a Nagios plugin and a MySQL database, where the events are sent to via adapters such as syslog, SNMP Trap or MS event log.
Then check_eventdb reads these events and reports errors (as specified in configuration) to Nagios. Via the EventDB front end, administrators can acknowledge the events which check_eventdb no longer needs to recognize or report to Nagios in the future.
What do you get in the download?
You get a set of scripts used to store SNMP/syslog/other event based information in a MySQL database. This EventDB package consists of:
* MySQL database structure
* EventDB web front end
* Nagios plugin
* Syslog-ng configuration snippets
How does it compare to other event loggers?
There are similar programs such as Tivoli and OpenView, but these are licensed and relatively expensive. From what I know, it is the only event handler for Nagios which can handle these types of events, work with syslog and MS event logs.
As a developer, what do you love about EventDB?
The fact that it’s so simple. It’s essentially a text filter based on a MySQL database.
EventDB’s simplicity allows it to be practically invulnerable to errors, and being based on such a reliable interface like MySQL, EventDB remains reliably robust.
EventDB in a nutshell?
EventDB is for administrators who require more detailed monitoring than what Nagios offers out of the box.
Monitoring software components is complex but necessary- especially for large environments.
Here an administrator need not write their own checks, they can simply download a pre-packaged event handler for free. It doesn’t get better than that.
More information:
Features & how EventDB works
Join the project or download
Ask the developer: NETWAYS Portal for Nagios

NETWAYS Portal for Nagios is basically a more user friendly alternative interface for Nagios, which allows much greater span for customisation especially in terms of user administration.
For the techies?
It is a set of Typo3 extensions, especially developed to offer a centralized view of complex, large scale Nagios monitoring environments. As it is based on XML templates and the main extension net_dbdata, it supports multiple Nagios instances and multiple NDO databases, while being also very flexible and configurable.
Why Typo3?
Being based on open CMS Typo3 allows user groups and user access rights to be configured and fine tuned. So for example in larger organisations views can be customised to vary by areas of responsibility or levels of management. It can even be connected to external authentication systems such as LDAP.
How does it work?
Nagios data is stored via NDO in a database where our net_dbdata extension reads host and service information, current status, alert and notification history, etc. This information is sent to the Portal and displayed. Commands given into the Portal are then sent to Nagios for execution via net_nagioscmd. Graphical representations of Nagios data are enabled with net_sproxy to display graphs or status maps from any source, such as NagiosGrapher or NagVis.
What’s new in version 3.0.1?
There are new views such as our SLA View and the Host Aggregated View. The SLA View displays host and server availability with an in built calendar to search periods of system availability. The Host Aggregated View gives an overview of all host states and number of errors collated one page, in a much clearer format.
What about useability?
We wanted to make interacting with Nagios clearer and easier so we added a few extras such as in screen comment windows (so you don’t have to leave the page to see the details), multi-commands and Ajax like search-selection fields.
What are multi-commands exactly?
The standard Nagios interface restricts the user to applying bulk commands to just hosts or their host groups. In the Portal, administrators can pick any individual host, host groups or service (simply by checking tick boxes) to apply Nagios commands to. Once they are selected, the command is carried out on all – as easy as a few clicks.
How is this interface for Nagios different from the others?
That would definitely have to be its greater customisation and configuration flexibility. Being able to handle multiple differentiated users, to create in essence a custom interface, with custom access rights for each user is definitely useful for larger organisations. Not only that, because it is based on TYPO3, it can integrate any application like wikis or ticketing systems. So it has a huge potential to extend beyond an interface for Nagios to a completely integrated monitoring environment.
The new NETWAYS Portal in a nutshell?
In all, it’s more user friendly – less clicking around to get to the information administrators need- and it’s simply more flexible.
More information:
Features & demo system
Join the project or download